how to check graphic card in pc
Introduction
Importance of Checking Graphic Card in PC
The graphic card, often referred to as the GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), plays a pivotal role in the overall performance of a computer. In today’s digital landscape, where consumption of high-resolution videos, immersive games, and elaborate graphical content is commonplace, ensuring your graphic card is functioning optimally is non-negotiable.
Just like a car needs regular maintenance to run smoothly, your computer’s graphic card also requires routine checks to prevent future issues. Whether you’re a gamer, an artist, or someone using the PC for everyday tasks, having a reliable GPU can dramatically enhance your experience. But why is it so critical to check on this component regularly?
- Performance Optimization: A well-functioning graphic card translates directly into faster graphics rendering, smoother frame rates, and an overall better user experience.
- Preventing Data Loss: Graphic card failures can lead to sudden crashes or system failures, which could potentially result in data loss. Regular checks can catch problems before they escalate.
- Gaming and 3D Rendering: For gamers and professionals working in graphic designing or video editing, the efficiency of the GPU can make or break your work.
- System Compatibility: As software and games evolve, they often require more advanced hardware. Checking the status of your graphic card ensures you can keep up with these demands.
In essence, being proactive rather than reactive can save both time and money and ensure an uninterrupted computing experience.
Common Signs of Graphic Card Issues
Recognizing the early signs of graphic card problems is crucial; unfortunately, many users only notice the symptoms when it’s almost too late. Reflecting on my own experience, I once ignored flickering graphics during intense gameplay, convincing myself it was just a minor glitch. A few weeks later, my entire system crashed, leaving me in a more troublesome situation than if I had acted sooner.
Here are some common signs to look for:
- Screen Artifacts: You may notice strange lines, shapes, or colors appearing on your screen, often indicating issues with the GPU. This can manifest as blocky images or random textures that shouldn’t be there.
- Frequent Crashes or Freezes: If your PC is suddenly crashing during simple tasks or freezing during graphical loads, it could be a clear sign of graphic card failure.
- Overheating: Excessive heat or noise from your graphics card can suggest that it’s working overtime or not cooling effectively; both situations could lead to longer-term damage.
- Poor Frame Rates and Lag: If your gaming or graphic-intensive activities suddenly become choppy, it may indicate that the graphic card is struggling to keep up with the workload.
- Driver Issues: Often, problems can arise from outdated or corrupted drivers. Regular updates are necessary, but when they fail, they can create instability in graphic performance.
- Black Screens: A complete black screen while using graphic-intensive applications can indicate that the GPU is having difficulty processing the necessary commands, leading to potential shutdowns.
By familiarizing yourself with these signs and performing regular assessments of your graphic card, you not only protect your investment but also streamline the overall performance of your PC. When problems arise, a quick check can often provide valuable insight into what may need immediate attention, preventing more invasive repairs down the line.
Remember – staying vigilant and proactive could be the difference between a simple fix and an unexpected hardware overhaul.
Basic Overview of Graphic Cards
What is a Graphic Card?
At its core, a graphic card, or GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), is a specialized hardware component responsible for rendering images, animations, and videos for the computer display. Essentially, it acts as the brain of visual processing, taking data from the CPU (Central Processing Unit) and transforming it into something you can see on your screen.
When I first built my gaming PC, I was initially clueless about the significance of choosing the right graphic card. I learned quickly that the GPU determines how well my system could handle demanding tasks, from gaming to graphic design. The intricacies involved with processing images and displaying them fluidly are what make modern graphic cards essential for anyone who values a smooth visual experience.
Here’s a breakdown of how graphic cards function:
- Rendering Graphics: The GPU translates complex data into images by breaking down scenes into pixels, making it possible for games and applications to render environments, characters, and various other elements visually.
- Enhanced Performance: Graphic cards provide parallel processing capabilities, allowing them to tackle multiple tasks simultaneously. This is especially useful when running modern applications and games that are designed to utilize multiple cores for enhanced performance.
- Storage and Memory: Most graphics cards come equipped with their own dedicated memory (VRAM), which is vital for storing textures and images that need to be processed quickly, facilitating faster load times and smoother gameplay.
Understanding what a graphic card is helps to clarify its significance in a computing environment. Whether you are gaming, editing videos, or simply watching high-definition content, this component makes sure you have the picture-perfect performance you desire.
Types of Graphic Cards
Graphic cards come in various types, and choosing the right one depends on your specific computing needs. Here’s a quick overview of the common types of graphic cards available in the market:
- Integrated Graphics:
- These are built into the CPU and share memory with it.
- Pros: Cost-effective, less power consumption, suitable for everyday tasks like browsing, office work, and video playback.
- Cons: Limited graphics performance; not ideal for intensive gaming or professional graphic applications.
- Dedicated Graphics Cards:
- These are standalone cards installed into a PCIe slot on the motherboard.
- Pros: Much higher performance tailored for gaming, video editing, and 3D rendering; has its own VRAM which allows for faster access to data.
- Cons: More expensive and requires sufficient power supply and space within the case.
- Workstation Graphics Cards:
- Designed specifically for professionals in areas such as graphic design and CGI rendering.
- Pros: Optimized for software applications like AutoCAD and Adobe Creative Suite; better stability and reliability.
- Cons: Higher price point due to specialized features; not typically needed by casual users or gamers.
- External Graphics Cards (eGPUs):
- These connect via USB-C or Thunderbolt ports and provide an external solution for laptops.
- Pros: Increased graphics performance for laptops without needing an upgrade internally; portable and flexible.
- Cons: Can be pricey, and performance may still be limited compared to internal dedicated options.
- Gaming Consoles with Integrated GPUs:
- While not exactly PC graphics cards, consoles come equipped with powerful integrated GPUs optimized for gaming.
- Pros: Tailored specifically for gaming with a consistent performance experience.
- Cons: Less versatility, as they aren’t designed for multifaceted tasks like general computing.
When I upgraded from integrated graphics to a dedicated GPU in my previous setup, the results were astonishing. The increased performance not only improved my gaming visuals but also reduced rendering times in graphic design projects. Being aware of these types helps users make informed decisions based on budget and intended use.
In conclusion, understanding the basic components and types of graphic cards allows users to tailor their setups to meet their specific needs, providing a significant boost to their overall computing experience. Whether for gaming, work, or creative endeavors, the right GPU can make a world of difference, enhancing not just performance but also enjoyment.
Checking Graphic Card in Windows OS
When it comes to ensuring that your graphic card is functioning optimally, checking its status in the Windows operating system is an essential step. There are several methods available to users, with two of the most straightforward options being Device Manager and the DirectX Diagnostic Tool.
Let’s dive into the specifics of how to use these tools effectively.
Using Device Manager
Device Manager is a built-in Windows feature that provides a comprehensive overview of all the hardware devices connected to your computer. Checking your graphic card through Device Manager is quick and easy, making it a great starting point.
Here’s how to do it:
- Access Device Manager:
- Right-click on the Start Menu button, or press Windows key + X to open the Quick Access Menu.
- Select Device Manager from the list.
- Locate Graphic Adapters:
- In the Device Manager window, scroll down to find Display adapters. Click on the little arrow to the left to expand this section.
- Here, you will see your graphic card’s name listed. For example, it might show something like “NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080” or “AMD Radeon RX 5600 XT.”
- Check Status:
- Right-click on the graphic card entry and select Properties.
- In the Properties window, navigate through the various tabs, especially the General tab which will tell you if the device is working properly. If there are issues, Windows will flag them under the Device Status box with error messages.
Using Device Manager not only allows you to check your graphic card’s status but also gives you insights into driver updates. If your GPU is outdated, you can often update it right from this window, ensuring you have the latest enhancements and fixes.
When I first encountered minor glitches in my games, a quick visit to Device Manager revealed that my graphic card driver was outdated. A mere update fixed the issues instantly, saving me from a more serious problem down the line.
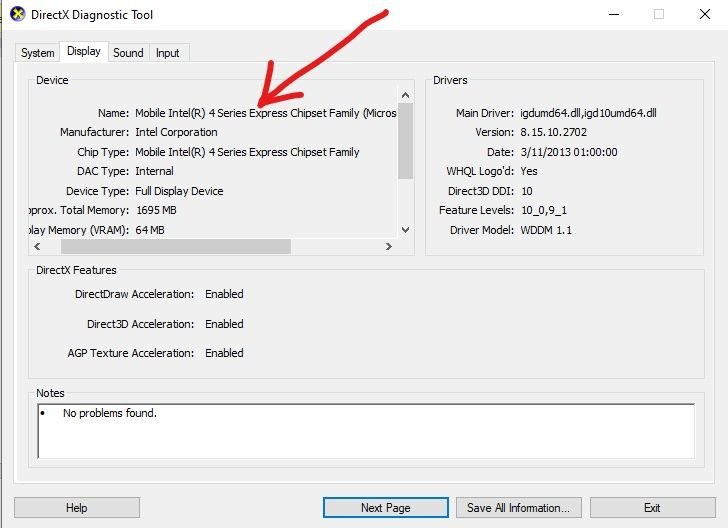
Checking with DirectX Diagnostic Tool
The DirectX Diagnostic Tool (DxDiag) is another valuable resource for checking the graphic card in your Windows system. This tool offers more detailed information about hardware components, including the GPU, which can help in diagnosing issues more thoroughly.
To access it, follow these steps:
- Run the DxDiag Tool:
- Press Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type
dxdiagand press Enter. This will launch the DirectX Diagnostic Tool.
- Display Information:
- Once the DxDiag tool is open, navigate to the Display tab.
- Here, you can find critical information about your graphic card, including the name, manufacturer, chip type, and even the amount of memory (VRAM) available. You’ll also see details on the driver version and date.
- Check for Issues:
- The tool runs automatic checks for any problems associated with graphic rendering. If you notice any red or yellow error flags, that might be a sign of deeper issues.
- Save Diagnostics (Optional):
- If you need to share or analyze the information later, you can click the Save All Information button, which generates a text file containing all the data shown in the tool.
For instance, during a particularly stuttery gaming session, I turned to the DxDiag tool to uncover that my GPU driver version was not just outdated; it was several generations behind. Updating the driver based on the info from DxDiag led to a significantly smoother gameplay experience.
Both Device Manager and DirectX Diagnostic Tool are powerful resources for monitoring graphic card health and performance in the Windows OS. Regularly checking these tools can provide peace of mind, ensuring your graphic card is ready to handle everything from everyday tasks to intensive gaming. Keeping an eye on your graphic card’s status can make all the difference, allowing for timely interventions that ultimately preserve your computing experience.
Checking Graphic Card in Mac OS
If you’re a Mac user, taking care of your devices and ensuring that hardware components like the graphic card are functioning properly is crucial for optimal performance. Fortunately, Apple provides user-friendly tools that make it easy to check your graphic card’s status. Two of the most effective methods are using the “About This Mac” feature and the System Information Utility.
Let’s explore both options in detail to make sure your Mac’s graphic capabilities are in top shape.
Using About This Mac Feature
The “About This Mac” feature is one of the simplest ways to view information about your graphic card and other vital hardware details on macOS. It’s a straightforward process that allows you to gather basic information quickly.
Here’s how to access it:
- Open About This Mac:
- Click on the Apple logo in the top left corner of your screen.
- Select About This Mac from the dropdown menu.
- View Graphics Information:
- A new window will open, displaying an overview of your Mac’s specifications.
- Click the System Report button to delve deeper.
- In the System Information window, look for the Graphics/Displays section listed on the left-hand side. This will list detailed information about your graphic card.
- Review Details:
- This section provides the name of the GPU, its total memory, and details of any additional displays connected (if applicable). If your Mac uses integrated and dedicated graphics, both will be listed here.
Using the “About This Mac” feature is excellent for a quick check. For instance, when I was trying to optimize games on my MacBook Pro, I learned that my integrated graphics were struggling with the latest titles. Simply corroborating that I had a dedicated GPU meant I could ensure it was activated for those games rather than relying solely on the integrated option.
Checking with System Information Utility
While “About This Mac” gives a general overview, the System Information Utility allows you to dive even deeper into the technical specifications of your graphic card and other components.
To access the System Information Utility, follow these steps:
- Open System Information:
- Again, start by clicking on the Apple logo in the top left of your screen.
- Go to About This Mac, and then click the System Report button.
- Explore Graphics and Displays:
- On the left sidebar, scroll down and click on Graphics/Displays under the Hardware section.
- Here, you’ll see extensive details about your graphic card, including the vendor, model, and graphics memory.
- Additional information like the display configuration, resolutions available, and even the performance metrics can also be explored.
- Performance Metrics (Optional):
- If you want to monitor real-time performance, you can also check the Activity Monitor (found under Applications > Utilities). It provides insights into GPU usage, memory pressure, and other statistics related to how your graphic card is performing while running applications.
During a recent graphics-intensive project, I faced unexpected lag, and a quick check with the System Information Utility illuminated that my GPU’s VRAM was nearly maxed out. This nudged me to optimize my workflow and close unnecessary applications to free up resources.
By frequently using both the “About This Mac” feature and the System Information Utility, Mac users can maintain an in-depth awareness of their hardware performance. These methods aren’t just a technical chore; they can enhance your computing experience, allowing for better gaming, video editing, and graphic rendering. So whether you’re a casual user or a professional content creator, keeping tabs on your graphic card in macOS is an essential practice that can lead to improved productivity and enjoyment.
Troubleshooting Common Graphic Card Problems
Graphic cards, much like any other component in a computer, can encounter issues that hinder performance and disrupt productivity. Whether you’re a gamer experiencing flickering graphics or a creative professional struggling with rendering delays, knowing how to troubleshoot common graphic card problems can save you a significant amount of time and frustration. Two essential aspects of troubleshooting are updating drivers and checking hardware compatibility.
Driver Updates
One of the most common culprits of graphic card issues is outdated or corrupted drivers. Drivers serve as the communication bridge between your operating system and the hardware—in this case, your graphics card. If they are not up to date, users can experience a range of problems from poor performance to outright crashes.
Here’s how to handle driver updates effectively:
- Check for Updates:
- For Windows, you can go to Device Manager, right-click your graphics card under Display Adapters, and choose Update driver. Opt for Search automatically for updated driver software to let Windows search for the most recent version.
- For Mac users, drivers are updated through macOS updates. Access this through System Preferences > Software Update.
- Manual Updates:
- For dedicated GPUs like NVIDIA and AMD, it may be beneficial to download drivers manually. Visit the manufacturer’s website, locate their drivers section, and input your graphic card model. This method often provides the latest enhancements and optimizations specifically designed for your hardware.
- Rollback if Necessary:
- Sometimes, newly installed drivers can create more issues than they solve. If that’s the case, you can roll back to a previous version of the driver through the Device Manager.
I can recall an instance where I was playing an online game, and the graphics suddenly began glitching. After investigating, I found out that the driver had not been updated for several months. A quick update resolved the issue, and I was back in the game without missing a beat.
Consistent driver updates not only maximize performance but also fix bugs and improve security, making this a crucial aspect of maintaining your graphic card’s health.
Hardware Compatibility Checks
Another frequent source of graphic card issues can stem from hardware incompatibilities. When upgrading components or building a PC from scratch, ensuring that your graphics card is compatible with the rest of your system is vital.
Here’s what to consider when performing hardware compatibility checks:
- Motherboard Compatibility:
- Ensure your motherboard has a compatible PCIe slot for your graphic card. Most modern GPUs require a PCIe x16 slot, so double-check your motherboard specifications before making a purchase.
- Power Supply Requirements:
- Graphic cards often require significant power. Check the wattage rating of your power supply unit (PSU) to ensure it meets the demands of your GPU. Also, ensure you have the necessary power connectors; some high-performance cards require additional PCIe power from the PSU.
- Cooling Solutions:
- High-end graphic cards can run hot, especially during demanding tasks. Make sure your case has adequate airflow and consider additional cooling solutions if your card runs hot—this could prevent thermal throttling and ensure you get optimal performance.
- Driver and OS Compatibility:
- Sometimes graphic cards may only be supported on certain operating systems. Always check that your OS is compatible with the GPU drivers and that recommended settings are in place for optimal performance.
When I built my first PC, I overlooked the PSU requirements and ended up with a card that performed inconsistently due to inadequate power. Making those compatibility checks upfront saved me from an array of frustration and performance issues later.
In conclusion, understanding the importance of driver updates and hardware compatibility checks is essential for troubleshooting graphic card problems effectively. Regular maintenance and awareness can help keep your system running smoothly, allowing you to focus on what truly matters—whether it’s gaming, designing, or simply enjoying your digital experience to the fullest. Being proactive can save time, prevent headaches, and ensure that you get the most out of your hardware investment.
Monitoring Graphic Card Performance
Once you’ve ensured that your graphic card is functioning optimally through regular checks and troubleshooting, the next step is to monitor its performance. Keeping a close eye on how your GPU operates under different conditions allows you to detect potential issues early and optimize performance as needed. Two key angles to explore in monitoring GPU performance are using third-party software and understanding performance metrics.
Using Third-Party Software
While both Windows and macOS provide built-in tools for checking graphic card performance, many users find that third-party software offers more robust and real-time capabilities. Various programs are designed to give detailed insights into GPU performance, temperature, memory usage, and more.
Here are some popular tools to consider:
- MSI Afterburner:
- Primarily used for overclocking, this tool provides real-time monitoring of your graphic card’s performance metrics.
- Users can track temperature, clock speeds, and load percentage while adjusting settings for optimal performance right within the software.
- GPU-Z:
- This lightweight application gives you a detailed breakdown of your GPU’s specs and can monitor various parameters in real time.
- It displays everything from GPU load and memory usage to temperatures, directly helping you keep tabs on your card’s performance.
- HWMonitor:
- A comprehensive monitoring tool that tracks all hardware performance, including graphics cards.
- It provides temperature monitoring, voltage readings, and fan speeds, making it indispensable for users wanting to monitor overall system health.
- Fraps or MSI Afterburner (for Gaming):
- If you’re primarily focused on gaming performance, programs like Fraps and MSI Afterburner can help ensure you’re maintaining optimal frame rates.
- These apps allow users to overlay real-time statistics directly on the game screen, providing valuable performance data while gaming.
When I was troubleshooting performance lags in an intensive game, using MSI Afterburner helped me ascertain that my GPU was overheating during peak gameplay moments. Adjusting the fan speeds significantly improved temperatures and ultimately enhanced performance.
These tools not only help monitor performance but also empower users to make informed decisions about cooling solutions and performance tweaks based on real-time data.
Understanding Performance Metrics
Monitoring performance is one aspect, but understanding the metrics you’re watching is just as crucial. Knowing what different metrics indicate about your GPU can help users interpret data effectively and respond appropriately.
Here are some key metrics to monitor and what they mean:
- GPU Load:
- A measure of how hard the graphics card is working. High GPU load during demanding tasks like gaming or rendering is expected, but consistent high loads while idle may indicate an issue.
- Temperature:
- One of the most critical metrics to watch. Most GPUs operate optimally between 60°C and 85°C. If temperatures exceed 90°C, this could lead to thermal throttling or damage.
- Fan Speed:
- Monitoring fan speed lets users ensure that the cooling system is functioning correctly. A sudden drop in fan speeds could correlate to rising temperatures and potential overheating problems.
- Memory Usage:
- VRAM (Video RAM) usage provides insights into how much memory your GPU is using during a session. If VRAM is consistently maxed out, it may affect performance, leading to stuttering or crashes in graphics-heavy applications.
- Frame Rates (FPS):
- Monitoring frame rates gives a direct measure of gaming performance. Higher FPS typically means a smoother visual experience. Low frames can indicate bottlenecks and may prompt performance tweaks or upgrades.
- Monitoring for Artifacts:
- While observing these metrics, also look out for visual artifacts, such as screen tearing or ghosting, which can indicate performance issues or driver-related problems.
Understanding these metrics not only helps you manage and optimize your graphic card effectively but also assists you in ensuring a stable and enjoyable computing or gaming experience.
In conclusion, monitoring graphic card performance is essential in maintaining optimal functionality and getting the most out of your hardware. By using the right third-party software and understanding the key performance metrics, you empower yourself to catch potential problems early, tweak settings for better performance, and ultimately enhance your overall experience, whether it’s gaming, designing, or enjoying media. Staying informed and proactive paves the way for smoother, more immersive computing adventures.
Upgrading or Replacing Graphic Card
Whether you’re seeking improved gaming performance, better video editing capabilities, or simply an enhanced graphical experience on your computer, upgrading or replacing your graphic card can make a world of difference. However, before getting your hands dirty, it’s essential to consider compatibility and follow the correct installation steps for a smooth transition.
Compatibility Considerations
When it comes to upgrading or replacing a graphic card, ensuring compatibility with your existing system is paramount. Here are some key factors to take into account:
- Motherboard Specifications:
- Check that your motherboard has the appropriate PCIe slot for the new graphic card. Most modern cards use a PCIe x16 slot.
- Additionally, verify whether the old card was using an older version, such as PCIe 2.0 or PCIe 3.0; newer cards are backward compatible, but knowing this can help manage performance expectations.
- Power Supply Requirements:
- Assess if your power supply unit (PSU) can handle the new GPU’s power requirements. High-performance cards often require significantly more wattage than older or integrated solutions.
- Look for the recommended wattage and additional power connector needs (such as 6-pin or 8-pin connectors) that your new graphics card may require.
- Physical Size of the Card:
- Graphic cards come in various sizes, including large, bulky models with substantial cooling solutions. Ensure that your case has sufficient clearance to accommodate the new card.
- Measure the internal space of your case before making a purchase. Also, consider airflow; a card with a large heatsink may affect the ventilation of nearby components.
- Compatibility with Other Hardware:
- If building a new system or upgrading old components, check the compatibility of other parts, such as the CPU and RAM. A bottleneck from other components can hinder the graphic card’s performance.
- Gaming and Software Requirements:
- If you’re primarily upgrading for gaming, review the recommended hardware specifications for the games you want to play. Some games may have specific GPU requirements that could steer your choices.
When I upgraded my GPU a while back, I overlooked my PSU’s wattage initially. Fortunately, I checked just in time and avoided purchasing an incompatible card that wouldn’t operate efficiently.
Being meticulous about compatibility ensures you won’t run into problems during installation and maximizes your new card’s performance.
Installation Steps
Once you’ve confirmed that your new graphic card is compatible, it’s time to dive into the installation process. Follow these steps to ensure a successful upgrade or replacement:
- Prepare Your Workspace:
- Begin by turning off your computer and unplugging it from the power source. Make sure you are working on a static-free surface; consider using an anti-static wristband.
- Open Your Case:
- Remove the screws or unlatch the panel of your computer case to access the internal components. Depending on your case, this can typically be done by removing two side panels.
- Remove the Old Graphic Card:
- If you are replacing a card, unclip the PCIe retention clip holding the old card in place and gently pull it out of its slot. Be cautious and avoid pulling it at an angle to prevent damaging the slot.
- Install the New Graphic Card:
- Align the new graphic card with the PCIe slot and gently press it down until it clicks into place. Make sure that the retention clip snaps back in to securely hold the graphics card.
- Connect Power Cables:
- If your new graphic card requires additional power connectors, plug them in accordingly. Ensure that all connections are secure.
- Close the Case:
- Once the card is in place, replace the side panels of your case and re-secure them.
- Install Drivers:
- Reconnect the power and turn on your computer. Once Windows loads, install the latest drivers for your new GPU from the manufacturer’s website to ensure optimal performance.
- Test the Installation:
- Open a game or graphic-intensive application to test the new GPU. Monitor temperatures and performance to verify that everything is functioning smoothly.
When I swapped out my graphics card, the exhilaration of launching a demanding game with upgraded graphics was unforgettable. The installation process became intuitive, and countless resources and forums helped me along the way.
In conclusion, upgrading or replacing a graphic card requires careful planning regarding compatibility and following specific installation steps. By considering these factors and taking the appropriate actions, you can enhance your computing experience significantly, paving the way for smoother gameplay, better design workflows, and immersive multimedia experiences. Remember, each upgrade is an investment not just in your computer, but in the experiences you’ll enjoy going forward.
Conclusion
Upgrading or replacing a graphic card can appear daunting, especially with the diverse range of options and compatibility considerations. However, understanding the nuances of this process is essential for maximizing your computer’s potential. As we have explored throughout this guide, monitoring performance, troubleshooting issues, and knowing when and how to upgrade are vital components of maintaining an optimal computing experience.
Recap of Key Insights
To wrap up, let’s review some of the critical points we discussed:
- Importance of Monitoring: Keeping an eye on your graphic card’s performance through tools and performance metrics ensures you can catch issues early. Monitoring not only aids in troubleshooting but also guides you on when it’s time to consider an upgrade.
- Understanding Compatibility: Before making a purchase, evaluating compatibility with your existing system is crucial. Checking the motherboard specifications, power supply requirements, and physical size of the new card can save you hassle and disappointments.
- Installation Steps: A straightforward installation process should be manageable for anyone, regardless of their technical background. Following the correct installation steps can help ensure that your new graphic card is properly set up to perform at its best.
- Personal Experiences Matter: Sharing personal anecdotes adds a relatable element to the process. From forgetting to check PSU wattage to the excitement of launching a new game post-upgrade, each experience can guide our understanding and decisions in future upgrades or troubleshooting efforts.
Looking Forward: The Benefits of Upgrading
Investing in a new graphic card can provide significant benefits, whether you are a gamer, a creative professional, or simply someone who enjoys watching high-definition content. Here are a few advantages you might experience when upgrading:
- Enhanced Performance: Newer graphics cards are designed with advanced technology and better performance capabilities, meaning games run smoother, videos stream flawlessly, and design software operates more efficiently.
- Improved Visuals: With advancements in GPU technology, upgrading can lead to improved texture resolutions, higher frame rates, and support for the latest graphic-intensive technologies such as ray tracing.
- Future-Proofing Your System: By investing in a quality graphic card, you effectively future-proof your system, making it ready to take on newer software and games that demand more processing power.
- Better Heat Management: Newer cards are often equipped with optimized cooling solutions, leading to quieter operation and cooler temperatures, which can extend the lifespan of your components.
- Multi-Display Support: If you’re into multitasking or gaming across multiple screens, a new GPU often comes with enhanced support for multi-display setups.
Reflecting on my experiences, upgrading my graphic card opened up an entirely new world in my gaming and design capabilities. The transition not only brought performance improvements but also revitalized my enthusiasm for my computing tasks.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, upgrading or replacing your graphic card is more than just a technical endeavor; it’s an essential part of maximizing your digital experience. Whether you’re enhancing your gaming sessions, streamlining your workflow, or simply enjoying a cinematic experience, taking the time to understand the process can lead to substantial long-term benefits.
Remember, when approaching your next graphic card upgrade, don’t hesitate to lean on the knowledge you’ve gained, share your experiences with others, and continue exploring the vibrant world of technology. With a little preparation and understanding, you can seamlessly transition to a more powerful and enjoyable computing experience, ensuring that you’re always ready for what’s next in the ever-evolving landscape of digital graphics. Embrace the journey, as every upgrade represents a step toward unlocking your system’s full potential!




