how to change pc name

How to Change PC Name on Windows 7
Open Control Panel and Access System Settings
To begin changing the name of a Windows 7 computer, the user needs to open the Control Panel. They can do this by clicking on the Start menu and typing “Control Panel” in the search bar. Once the Control Panel window opens, it’s important to ensure that the view is set to “Category” or “Large icons” for easier navigation. The user then needs to locate and click on the “System” icon. This action will take them to the System settings, where they can view important information about their PC, such as the operating system version and system specifications. In this section, they will find details about the current computer name and other network settings.
Rename PC and Restart to View Changes
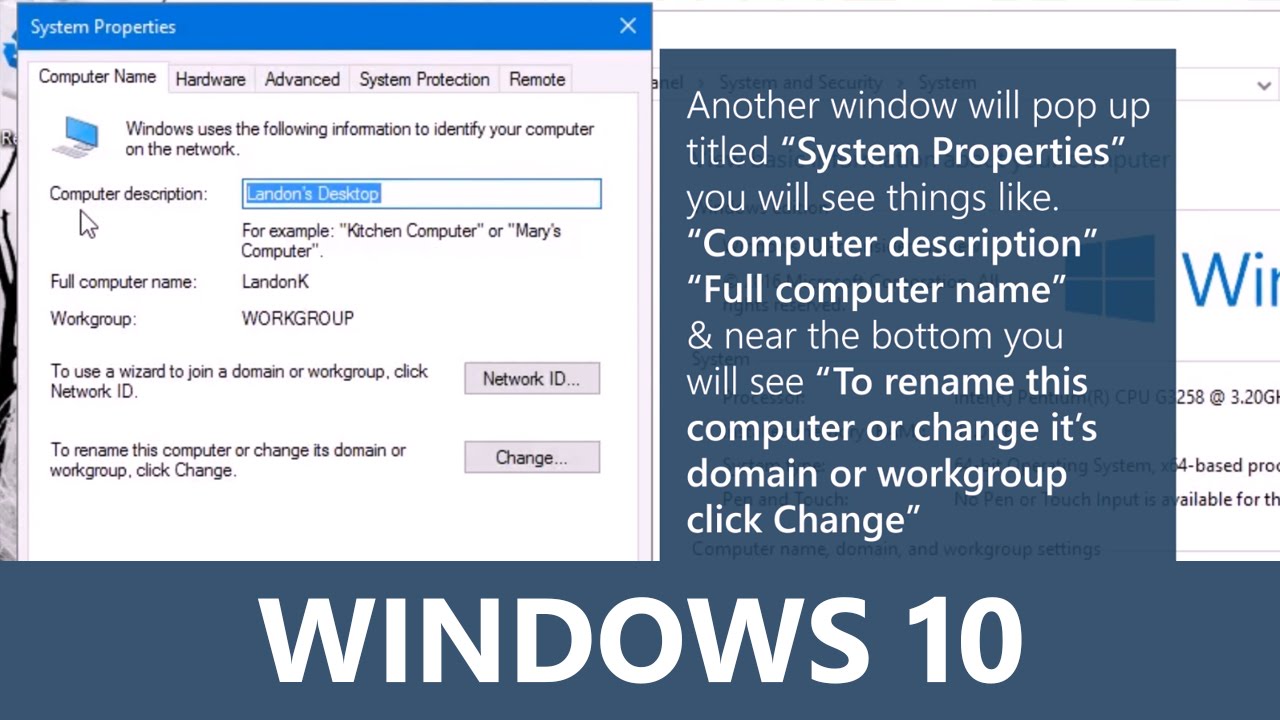
Once in the System settings, the user needs to look for the “Computer name, domain, and workgroup settings” section. In this section, there is a link labeled “Change settings.” Clicking on this link opens the System Properties window. Here, they will see an option to change the computer name. The user should click on the “Change” button, which allows them to enter a new name for their PC. It is crucial to keep in mind that the new name must adhere to certain guidelines: it should not exceed 15 characters, and it should only include letters, numbers, and hyphens. After entering the preferred name, the user clicks “OK” to confirm the changes. A prompt will appear informing them that a restart is required for the changes to take effect. The user must restart their PC and sign back in to view the new name. This process is straightforward and effectively personalizes their device, making it easier to identify when interacting with a network or other computers.
Importance of Renaming Your PC
Improved Network Identification
Renaming one’s Windows device can significantly improve network identification. When multiple computers are connected to the same network, default names generated by manufacturers often lead to confusion. For instance, a group of devices with generic names like “DESKTOP-CHDE8SR” can make it challenging to determine which machine is which during file sharing or remote desktop sessions. A well-chosen name makes it simpler to identify specific devices, ensuring easier management, collaboration, and connectivity especially in office or home environments with several computers. A unique name not only streamlines these processes but also aids in troubleshooting and support, allowing users and technicians alike to quickly reference the correct device.
Personalization and Organizational Benefits
Personalization plays a crucial role in enhancing user experience, and renaming a PC is an excellent way to achieve that. A custom name can reflect personal preferences, interests, or even the purpose of the device. For example, naming a laptop “TravelLaptop” provides immediate clarity regarding its primary use. Furthermore, personalization encourages users to feel more connected and responsible for their devices, which can foster better care and maintenance.
Organizationally, renaming PCs is beneficial in environments where multiple users share devices or when IT professionals manage many computers. Deploying a standardized naming convention can assist in overseeing assets, making inventory checks, and simplifying device updates or repairs. Naming PCs after the user or location, such as “Johns-Office-PC” or “Conference-Room-Computer,” ensures that responsibilities and ownership are clear. Such practices can also help prevent mix-ups and reduce downtime caused by misidentification.
In addition, following best practices when naming devices—like keeping names concise (ideally under 15 characters) and avoiding special characters—contributes to overall system performance and compatibility within a networked environment. When devices share a coherent naming scheme, it enables easier access, management, and security monitoring, ultimately leading to smoother operation and more efficient user experiences in both personal and professional settings.
Steps to Rename Your PC on Windows 8.1
Access PC Info and Select Rename PC Option
To rename a Windows 8.1 PC, the user should begin by accessing the Charms bar. This can be done by moving the mouse cursor to the upper or lower right corner of the screen to reveal the Charms menu. Next, the user should click on the “Settings” icon. Afterward, they should scroll down and click on the “Change PC settings” link located at the bottom of the settings menu. Once in the PC settings, users will find a left pane where they need to select the “PC and devices” category. From there, it’s essential to click on the “PC info” option at the bottom of this section.
In the PC info view, the user will see a prominent “Rename PC” option. Clicking this option allows the user to enter a new name for the computer. It’s important for the name chosen to comply with specific guidelines, such as being concise and avoiding special characters, to ensure compatibility within the network environment. After typing the desired new name, the user must click on the “Next” button to confirm the change. This process is straightforward and typically takes only a few moments to complete.
Restart PC for the New Name to Take Effect
Once the new name has been entered and confirmed, the final step involves restarting the computer. A prompt will usually appear, asking the user whether they would like to restart the device now or later. Restarting the computer is crucial, as the system needs to refresh to recognize and implement the new name properly. If the user opts to restart later, they should remember that the name change will not reflect until they restart their PC.
After the restart, the new name will be visible across the system and the network. This change will help to easily identify the device on a network, making it more manageable and organized. Users may notice the name reflected in various settings, such as network identification, file sharing menus, and when connecting to other devices. Overall, renaming a PC on Windows 8.1 is a simple yet effective process for users looking to personalize their computing experience and enhance organizational efficiency.
Benefits of Updating from Windows 8.1
End of Technical Support
Transitioning from Windows 8.1 to more recent operating systems such as Windows 10 or Windows 11 holds significant importance due to the end of technical support for Windows 8.1. The cessation of support means that users will no longer receive security updates, bug fixes, or technical assistance from Microsoft. This lack of support can expose users to security vulnerabilities, increasing the risks of malware attacks and unauthorized access to their data. By upgrading to a newer version, individuals can benefit from ongoing updates that help keep their systems secure and robust against emerging threats.
Enhanced Features in Windows 10 or Windows 11
Upgrading to Windows 10 or Windows 11 introduces users to a host of enhanced features designed to improve both usability and productivity. Windows 10 offers improvements such as a revamped Start Menu, integrated Cortana assistance, and the introduction of Windows Hello for biometric security. Meanwhile, Windows 11 takes these enhancements further with a redesigned interface that promotes ease of use. Features such as Snap Layouts for multitasking efficiency, DirectStorage for faster load times in gaming, and redesigned notification and settings menus enhance users’ overall experience.
Furthermore, Windows 11 introduces better integration with other Microsoft services like Microsoft Teams, enabling seamless communication and collaboration among users. The improved Microsoft Store in Windows 11 also facilitates easier access to a wider array of applications, providing numerous productivity and entertainment options. The transition from Windows 8.1 to either Windows 10 or Windows 11 consequently ensures that users can take advantage of modern functionality and advanced security settings, promoting a more streamlined and enjoyable computing experience.
In summary, embracing the move from Windows 8.1 to newer Windows versions not only mitigates security risks but also introduces users to an array of features designed to enhance their daily computing tasks. While some users may have grown comfortable with Windows 8.1, the increased efficiency, practicality, and ongoing support associated with updating can significantly enhance their technology experience. Upgrading thus represents an essential step towards maintaining a secure and productive digital environment.
How to Upgrade from Windows 8.1 to Windows 10
Backup Your Data Before Upgrade
Before initiating any upgrade process, it is vital for users to back up their important data. This process ensures that valuable files, documents, and settings are safe in case anything goes wrong during the upgrade. Users can utilize external hard drives, cloud storage solutions, or built-in Windows backup features to create a restore point. By having a backup in place, individuals provide themselves with peace of mind, knowing that critical data won’t be lost during the transition. It is essential to take this precaution seriously and allocate adequate time to ensure that everything important is copied and stored securely.
Follow Step-by-Step Upgrade Instructions
To upgrade from Windows 8.1 to Windows 10, users should first ensure that their PC meets the system requirements for the new operating system. This includes having a compatible processor, sufficient RAM, and available storage space. After confirming compatibility, users can visit the official Microsoft website to download the Media Creation Tool, which facilitates the installation process.
Once the tool is downloaded, users should launch it and select the option to upgrade this PC now. Following this, the tool will verify the existing system and download the necessary files for installation. It is essential for users to select their language, edition, and architecture (32-bit or 64-bit) during this process. After the download completes, the tool will guide users through a series of prompts, including accepting the license terms and choosing whether to keep personal files and apps or start fresh with a clean installation.
As the installation progresses, users will notice that the system may restart several times. During this phase, it is crucial for individuals not to interrupt the process to avoid issues. After a successful installation, the system will boot into Windows 10, requiring users to go through a short setup process, which includes choosing privacy settings and signing in with a Microsoft account.
Once the setup is complete, users should check for any available updates to ensure that the system runs optimally. This step guarantees that the new operating system is equipped with the latest security updates and features. By carefully following these steps, users can transition smoothly from Windows 8.1 to Windows 10, enjoying the enhanced functionality and support that comes with the latest software version.
Key Features of Windows 10 and Windows 11
Improved Security Measures
Windows 10 and Windows 11 introduce significant security enhancements that address modern threats. Both operating systems feature Windows Defender, which provides real-time protection against malware and viruses. This built-in antivirus system continually updates its definitions to protect against the latest threats. Additionally, Windows Hello allows users to log in using biometric data such as facial recognition or fingerprints, adding a layer of security. Furthermore, features like BitLocker offer full-disk encryption, allowing users to secure their sensitive data from unauthorized access. Enhanced firewall settings and secure boot mechanisms further ensure that users’ systems remain protected from a variety of cyber threats.
Enhanced User Interface and Productivity Tools
The user interface of Windows 10 and Windows 11 marks a shift toward a more intuitive design. Windows 10 retains familiar elements while introducing the new Start Menu, which combines traditional app shortcuts with live tiles for quick access to important information. Users can customize this menu to suit their workflow. Windows 11 enhances this experience with a centered Start Menu and redesigned taskbar, offering a cleaner and more modern aesthetic. The introduction of Snap Layouts and Snap Groups allows users to efficiently organize and manage multiple open windows, promoting enhanced productivity.
Moreover, the integration of Microsoft Teams into Windows 11 facilitates better communication and collaboration, particularly for remote work and online meetings. Both operating systems also come with a revamped Microsoft Store, making it easier for users to discover and download applications tailored to their needs.
Beyond visual changes and usability improvements, both systems provide a range of productivity applications such as the updated Microsoft Edge browser, which offers features like vertical tabs and improved performance. The support for touch, pen, and voice input further expands the ways users can interact with their devices.
All these enhancements culminate in a computing environment designed with user experience in mind, focusing on efficiency, ease of navigation, and streamlined workflows. By embracing these advancements, users can take advantage of modern technology tailored to meet the demands of today’s digital landscape.
System Requirements for Windows 10 and Windows 11
Minimum Hardware Specifications
To effectively run Windows 10 and Windows 11, certain minimum hardware specifications are essential. Windows 10 requires a 1 GHz or faster processor, with at least 1 GB of RAM for the 32-bit version or 2 GB for the 64-bit version. In terms of storage, a minimum of 16 GB is necessary for the 32-bit OS and 20 GB for the 64-bit OS. Furthermore, the device should support DirectX 9 or later with a WDDM 1.0 driver, and the display must have at least 800 x 600 resolution.
Windows 11 has slightly higher requirements to provide a more streamlined performance. It necessitates a compatible 64-bit processor with at least 1 GHz and two or more cores; a minimum of 4 GB of RAM; and at least 64 GB of storage space. Moreover, Windows 11 requires TPM (Trusted Platform Module) version 2.0 for enhanced security features, alongside UEFI firmware that supports secure boot capabilities. The graphics card must be DirectX 12 compatible, and the display resolution needs to be a minimum of 720p.
Compatibility Check Tool Availability
To help users determine whether their devices meet the requirements for Windows 10 or Windows 11, Microsoft offers a compatibility check tool. This tool, known as the PC Health Check app, allows users to verify all essential specifications against the OS requirements. By running the application, users receive a detailed report on their device’s compatibility status and necessary upgrades, if any are required.
This tool proves valuable for those considering an upgrade, as it provides clarity about whether existing hardware can support the newer operating system without needing significant changes. Users can easily download the PC Health Check app from Microsoft’s official website. The straightforward interface guides users through the compatibility process, empowering them with informed decisions regarding system upgrades or replacements.
In summary, understanding the hardware specifications and utilizing the compatibility tools available from Microsoft equips users with the necessary information to ensure their devices are ready for the continued evolution of Windows operating systems.
Final Thoughts and Recommendations
Consider Upgrading Your PC for Better Performance
Upgrading to a new operating system such as Windows 10 or Windows 11 can offer substantial improvements in performance and capabilities. Users running older versions, like Windows 7 or Windows 8.1, may find their hardware lacking when it comes to supporting more advanced features or the latest applications. Newer PCs usually come equipped with better hardware, including faster processors, increased memory, and enhanced graphics capabilities, which can lead to smoother operation and more efficient multitasking. The improvement in performance is particularly noticeable during demanding tasks such as gaming, video editing, or heavy multitasking.
Choosing to upgrade can also provide access to major new features and security updates. Modern operating systems come with a host of built-in functionalities to help enhance user experience and productivity, such as virtual desktops, improved file management systems, and integration with cloud services. With the increasing emphasis on remote work, having a capable operating system is essential for efficient collaboration and communication. Upgrading not only heightens the device’s overall performance but also ensures that users remain compatible with current technological advancements and application requirements.
Seek Assistance for a Smooth Transition to New Operating Systems
Transitioning to a new operating system can sometimes be a daunting task, especially for users who may not be as technologically savvy. To ensure a seamless upgrade process, it is often beneficial to seek assistance from professionals or knowledgeable friends who can guide through the installation steps. Familiarize oneself with the backup process before making any significant changes. This precaution helps guarantee that personal files and important data are secure in case anything goes wrong during the upgrade.
Moreover, users should consider exploring online resources and forums that provide insights and solutions to common upgrade issues. These platforms can offer support from experienced community members who have faced similar challenges. Taking advantage of tutorial videos or step-by-step guides can make the initial setup much easier. After an upgrade, users may require time to acclimate to the new features and functionalities, and accessing customer support or community discussions can help ease the transition. By doing so, users ensure they harness all the advantages that come with a new operating system while minimizing potential frustrations associated with the change.




